Budget from a Polity Angle
Department of Economic affairs under Finance Ministry prepares Budget.
1. Word budget is mentioned in the constitution of India. Annual Financial statement is the term used for Budget
Budget contains
1. Estimate Revenue receipts
2. Estimate of Capital receipts ( meaning will be seen in economy part of Budget)
3. Ways and means to raise revenue
4. estimates Expenditure for revenue and capital receipts
5. Previous year actual receipts and expenditure.
6. Reasons for deficit or surplus in the previous year than estimates
7. Economic policy of Gov. Tax proposals, schems and initiatives
Types of Funds
1. Consolidated Fund of India
2. Public account of India
3. Contingency fund of India
Consolidated Fund of India
Incoming :
1. Consists of all revenues from Taxes + Loans + Repayment of loans
Outgoing :
1. Charged on CFI - Cannot be amended by Parliament. Only discussed
2. Made from CFI - Appropriations act
Public account of India :
1. Gov acts as a Banker to this account coming from Provident funds and small
2. operated by executive action - no need of parliament approval
Contingency fund ;
1. lies with Finance secretary on behalf of President
2. opearted by executive action
Parliamentary processes in Budget
1. Presentation of Budget
2. General discussion
3. Scrutiny of Departmental committess
4. Voting on demands for Grants
5. Passing of Appropriation Bill or running Bill or Supply bill
6. Passing of finance Bill
I.Presentation of Budget :
1. Read by Finance minister in Lok Sabha
2. Laid in Rajya Sabha after Lok Sabha. RS has no power to vote on the demands for grants
II General Discussion :
1. Takes place in Both the houses of Parliament
2. No cut motion or no vote. FM can reply at the end
III Scrutiny by Departmental Committees :
1. 24 Departmental committees of Parliament examines the demand for grants
2. Submitted to both the houses for consideration
IV Voting on Demands for Grants
1. In the light of the Departmental Standing committee, Loksabha ( exclusive previlege of Loksabha) takes up voting of demands
2. Demands are presented ministry wise
3. A demand becomes a grant after it has been duly voted
4. Votable part of the Budget can only be voted. Expenditure charged on the consolidated fund of India is not voted
5.
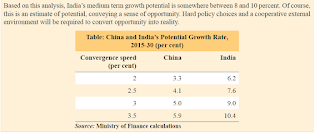
 3rd method would be more suitable. " Correlation between Institutions and Growth " . India and China are outliers and they could convergence.
3rd method would be more suitable. " Correlation between Institutions and Growth " . India and China are outliers and they could convergence.